
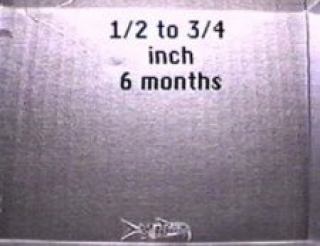
 Juveniles are very slow growing
Juveniles are very slow growing Parents in spawning site
Parents in spawning site Eggs partially hatched after 30 hours
Eggs partially hatched after 30 hours Newly hatched fry
Newly hatched fry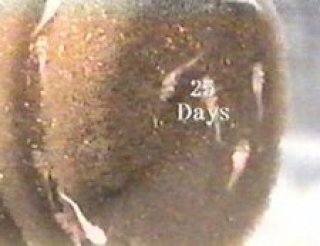 Fry after 25 days
Fry after 25 days Tank raised juveniles
Tank raised juveniles Adult male
Adult male Video - Pink colour morph
Video - Pink colour morph Video spawning
Video spawning Adult
Adult Male (on right) chasing gravid female
Male (on right) chasing gravid female Spawning in the open
Spawning in the open Gravid female
Gravid female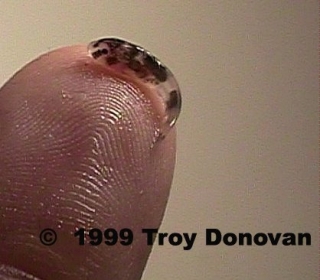 Fry
Fry

 Pair - female on left
Pair - female on left


 Close-up of head
Close-up of head Juvenile
Juvenile
 All Fishes Data Sheet All Fishes Data Sheet | |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Synodontis lucipinnis Wright & Page, 2006 |
| Common Names | Dwarf Lake Syno Dværggøgemalle (Denmark), False Cuckoo Catfish, Petricola Dwarf Syno, Pink Dwarf Lake Syno |
| Type Locality | Musende Rocks, Zambia, Lake Tanganyika, 8°46'00''S, 31°07'00''E. |
| Synonym(s) | |
| Pronunciation | sin oh don tiss |
| Etymology | According to Cuvier, Synodontis is an "ancient name for an undetermined fish from the Nile". It is not derived, as often reported, from syn-, together and odous, tooth, presumed etymology of the lizardfish genus Synodus and refers to the closely-spaced lower jaw teeth of both genera. |
 Species Information Species Information | |
| Size | 79mm or 3.1" SL. Find near, nearer or same sized spp. |
| Identification | All species in the genus Synodontis have a hardened head cap that has attached a process (humeral process) which is situated behind the gill opening and pointed towards the posterior. The dorsal fin and pectoral fins have a hardened first ray which is serrated. Caudal fin is always forked. There is one pair of maxillary barbels, sometimes having membranes and occasionally branched. The two pairs of mandibular barbels are often branched and can have nodes attached. The cone-shaped teeth in the upper jaw are short. S-shaped and movable in the lower jaw. These fish produce audible sounds when disturbed rubbing the base of the pectoral spine against the pectoral girdle. All species in the genus Synodontis have a hardened head cap that has attached a process (humeral process) which is situated behind the gill opening and pointed towards the posterior. The dorsal fin and pectoral fins have a hardened first ray which is serrated. Caudal fin is always forked. There is one pair of maxillary barbels, sometimes having membranes and occasionally branched. The two pairs of mandibular barbels are often branched and can have nodes attached. The cone-shaped teeth in the upper jaw are short. S-shaped and movable in the lower jaw. These fish produce audible sounds when disturbed rubbing the base of the pectoral spine against the pectoral girdle. |
| Sexing | First lay the fish in your hand with its head toward your palm and the tail toward your fingers. Hold the dorsal spine between your middle and ring finger so the fish is belly up and you won't get punctured by the sharp fin spines (which hurts - be careful). The genital pore is in a small furrow of tissue (in healthy fish) and will be obstructed by the pelvic fins. Pull down on the tail gently to arch the fish's spine and the pelvic fins will stand and the furrow open to display the genital pore and the anus of the fish. The male has a somewhat ridged genital papillae on which the spermatoduct is on the back side, facing the tail fin. A gravid female will also show an extended papillae but the oviduct is on the ventral side of the papillae. It may also show a little redness if gravid. A thin or emaciated female will have just two pink pores, the oviduct and the anus. First lay the fish in your hand with its head toward your palm and the tail toward your fingers. Hold the dorsal spine between your middle and ring finger so the fish is belly up and you won't get punctured by the sharp fin spines (which hurts - be careful). The genital pore is in a small furrow of tissue (in healthy fish) and will be obstructed by the pelvic fins. Pull down on the tail gently to arch the fish's spine and the pelvic fins will stand and the furrow open to display the genital pore and the anus of the fish. The male has a somewhat ridged genital papillae on which the spermatoduct is on the back side, facing the tail fin. A gravid female will also show an extended papillae but the oviduct is on the ventral side of the papillae. It may also show a little redness if gravid. A thin or emaciated female will have just two pink pores, the oviduct and the anus. |
 Habitat Information Habitat Information | |
| Distribution | Africa African Waters, Western Rift Valley Lakes, Tanganyika (click on these areas to find other species found there) Login to view the map. |
| IUCN Red List Category | Not Evaluated |
| pH | 6.5 - 8.5 |
| Temperature | 22.0-24.0°C or 71.6-75.2°F (Show species within this range) |
| Other Parameters | Surprisingly this species reproduces in less than neutral pH water condition much removed from those found in it's native habitat. |
 Husbandry Information Husbandry Information | |
| Breeding Reports | There is no breeding report. |
 Further Information Further Information | |
| Reference | Bulletin of the Florida Museum of Natural History v. 46 (no. 4), pp 126, Figs. 4A, 19 |
| Wishlists | Love this species? Click the heart to add it to your wish list. There is no wish to keep this species. |
| Spotters | Spotted this species somewhere? Click the binoculars! There are 5 records of this fish being seen, view them all. |
 More Resources More Resources | |
| Forum BBCode | |
| Look up S. lucipinnis on PlanetCatfish.com | |
 | Look up S. lucipinnis on Fishbase |
 | Look up S. lucipinnis on Encyclopedia of Life |
 | Look up S. lucipinnis on Global Biodiversity Information Facility |
| LFS label creator ARN ref:1.13.29.103 | |
| Last Update | Thu Jan 01, 1970 1:00 am (Species record created: Thu Jan 01, 1970 1:00 am) |
